Cast Aluminium vs Cast Iron:
What You Need to Know
In manufacturing, debates between materials seem to focus mostly on casting cast aluminium vs cast iron. Even though they both get cast almost similarly, both have significant differences in properties, applications, and benefits. It can range from cookware, industrial machinery, and much more, all of which have their strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these differences will help you make an informed choice tailored to your needs. This blog will talk about the difference between cast iron and cast aluminium, their benefits, and where each is better suited for a specific application. Let’s get into it!
Table of Contents
What are Cast Aluminium?
Cast aluminium is broadly defined as a versatile metal in which liquid aluminium is poured into moulds and solidified within them. It is often alloyed with other elements, such as silicon, magnesium, or copper, where it can acquire greater strength and heat resistance. Lightweight yet strong, it is widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and cookware manufacturing. Its natural corrosion resistance due to the fact that an oxide layer is naturally formed on its surface makes it suitable for outdoor and marina appliances.
What are Cast Iron?
Cast iron is an alloy of iron and carbon, with more than 2% carbon. It is produced by the melting of iron and casting in moulds. Cast iron has earned appreciation due to its great ability to retain heat and wear resistance. Some members of this family are gray iron, ductile iron, and white iron, with some different uses. For example, tensile strength and plasticity are tremendous in ductile iron. Cast iron, however, is highly machinable. On the other hand, cast iron is heavier and also more brittle compared to aluminium. It easily breaks into cracking when struck under impact.
What are Some Advantages of Cast Aluminium?
Cast aluminium has numerous benefits that have made it one of the top choices in many industries:
- Light: Well lighter than cast iron, though it is economical to transport and ideal for applications where weight seems a factor.
- Corrosion Resistant: It guards the material against rust and corrosion as the natural oxide layer protects it, and it is excellent for outdoor use.
- Heat Conduction: Not retaining heat as cast iron does. This conducts heat wonderfully for cooking.
- Cost: It is less expensive as it has lower manufacturing costs and largely available raw materials.
- Recyclable: Cast aluminium is non-polluting and can be recycled with no loss in its properties.
What Are Some Advantages of Cast Iron?
Cast iron with such extraordinary properties has a very special niche in different applications for industries:
- Excellent Retention of Heat: It provides excellent heat retention, which makes it suitable for cooking utensils and heating applications.
- Strength: Though heavier, the tensile strength and durability it offers are exceptional.
- Machinability: Cast iron has good machinability, therefore allowing finer shaping and detail work.
- High-wear Resistance: Performs well in highly stressful applications, for example, mechanical parts and construction equipment.
- Durability Cost Effective: Although cast aluminium is a bit costlier when purchased, cast aluminium can save more in the long run because of its better durability.
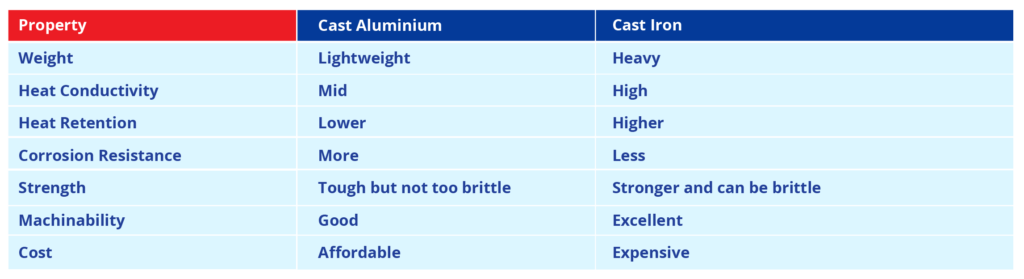
Cast Iron Vs. Cast Aluminium: Key Differences!
Let us compare the difference between cast iron and cast aluminium:
Varieties of Cast aluminium vs. Cast Iron
Cast Aluminium Varieties:
- Die-cast aluminium: Having high accuracy and a surface finish that is very smooth
- Permanent mould cast aluminium: High in Strength and High Resistance
- Aluminium sand cast: Applications in mass production and complexity greater
Cast Iron types:
- Gray Iron: Provides excellent machinability and Resistance to wear and Tear.
- Ductile Iron: Strong, yet flexible.
- White Iron: Tough and abrasion-resistant.
- Malleable Iron: Heat-treated for increased ductility and tensile strength.
Cast Aluminium Vs Cast Iron: Which One to Choose?
Choosing between cast aluminium vs cast iron depends on your project’s specific requirements. Here are some decision points:
- Weight: If weight is a concern, cast aluminium is the better option.
- Heat Retention: For applications requiring sustained heat, cast iron is superior.
- Corrosion Resistance: For outdoor or marine use, cast aluminium is more durable.
- Cost: Cast aluminium is generally cheaper, especially for mass production.
- Strength: If strength is an issue, weigh the aluminium vs iron strength trade-offs carefully.
Can Cast aluminium or Cast Iron Be Recycled?
Both can be recycled, but it varies a bit in the process:
- Cast Aluminium: It is highly recyclable and doesn’t lose its properties even on reprocessing. It is, therefore, an eco-friendly material.
- Cast Iron: Even though requiring less energy during recycling, the issue is that it cannot be easily manufactured as with aluminium because it is brittle.
Conclusion:
Evidently, the choice between cast iron vs aluminium would depend on the requirements of the industry. For instance, with aluminium, one would like lightness and resistance to corrosion, but with iron, heat retention and strength are much more important. Thus, AKP Ferrocast remains one of the most prominent organisations for industries with extremely high demands in terms of durability and flexibility since the company specialises in castings of ductile and grey iron, satisfying international needs in quality and precision. Additionally, AKP Ferrocast also offers Forged and Cast Iron solutions to meet diverse industrial needs with enhanced strength and reliability.
Frequently Ask Questions
What is Cast Aluminium used for?
It has been used for various car parts, cookware, machinery, and construction because of its lightness, corrosion resistance, and temperature resistance. This is applied in various parts such as engine blocks, frying pans, and industrial equipment where durability and thermal conductivity are important.
What is the best-casting Aluminium Alloy?
Silicon and magnesium-containing ones, such as A356 or 6061, are among the best aluminium alloys for casting. These alloys are very strong, have high resistance to wear, and are light, which explains why they find wide applications in aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries that require high strength and accuracy.
Is cast iron better than Aluminium?
Depending on the application, cast iron vs aluminium block is selected. Cast iron is used in applications where retention of heat is necessary, such as cookware or machinery, because iron is stronger than aluminium. Cast aluminium is lighter and corrosion-resistant and thus suitable for use in automotive parts, aerospace, and portable products.
Does Cast Aluminium Rust?
No, cast aluminium does not rust because it is composed of iron. However, cast aluminium is developed by a natural oxide layer, which keeps the product away from corrosion, so this kind of cast metal product remains strong even if kept outdoors or in wet environments for many years.
Which material is easier to Machine: Cast Iron Heads vs Aluminium?
Casting aluminium is softer and less dense than cast iron and, therefore, easier to machine at faster cutting speeds. Cast iron is better in surface finish and dimensional stability. Hence, for high-precision applications requiring more durability, cast iron is used.
