Cast Iron vs Cast Steel:
Key Differences and Applications
Selecting between cast iron vs cast steel when sourcing materials for manufacture, construction, or engineering is important. The variety of properties both metals portray makes them suitable for different uses. These materials may seem to be similar. However, they possess significant differences in their characteristics and serve different purposes in many applications. This difference is based on their composition, basically in the amount of carbon, silicon, manganese, phosphor, and sulfur that both of these metals have. In this blog, we will discuss what cast iron and cast steel are, the difference between cast iron and steel, their applications, and benefits.
Cast iron, being pretty hard and brittle, is most suitable for products that are mechanically robust and have wear resistance. Then, what is cast steel? Cast steel has high levels of toughness, plasticity, and impact resistance, which make it a suitable product for components that experience stresses and strains. Cast iron and cast steel are not competitors. In fact, each type of alloy is ideal for use in different situations. The primary consideration here is the selection of the appropriate material for a given product with the right combination of strength and efficiency in the production process.
Table of Contents
What is Cast Iron?
Cast iron is an alloy of iron and carbon and has a carbon percentage of 2% – 4%. It is also made up of silicon and manganese. It contains traces of phosphorus and sulfur as impurities. The molten iron that has been produced is then poured into molds, where it cools down to form its shape. It is used for its excellent heat-retaining properties, high durability and high compressive strength. Cast iron is used for the manufacture of applications that need robustness and stability.
What is Cast Steel?
Cast steel is also an iron-carbon alloy that contains a lesser percentage of carbon, usually between 0.15% and 2%. It also contains small amounts of silicon, manganese, iron sulfides and phosphides. But can you cast steel and what are their unique character traits? Yes, you can cast steel. This cast steel is characterized by high tensile strength, ductility, and shock resistance. It is ideally suited for application in the construction industry and transport industries.
Key Differences Between Cast Iron and Cast Steel

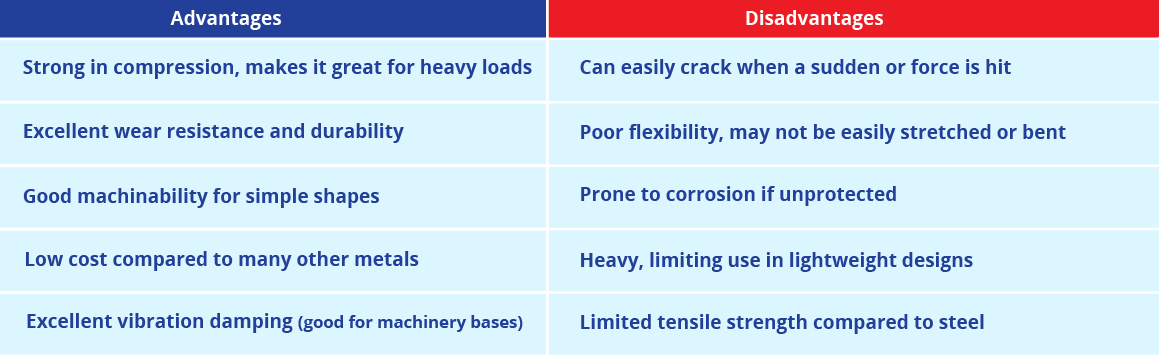
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cast Iron
Cast iron is used for the manufacture of components and parts in various industries that need incredible strength. It is highly resistant to pressure and heat, which makes it suitable for use in large machinery and construction equipment as well as infrastructures.
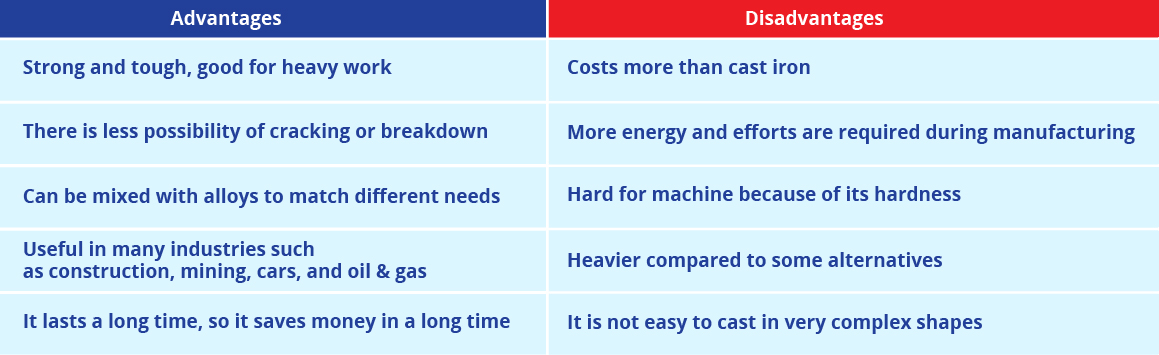
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cast Steel
Due to its prevention and high tensile strength, cast steel is used extensively in various manufacturing fields. It can be easily molded into various forms and is perfect for accurate designs.
Which One to Choose - Cast Iron or Cast Steel?
When deciding between cast iron or cast steel, it is best to consider your project demands. Cast iron prefers to be known for applications requiring good wear resistance and heat retention at low cost. Cast steel, however, shines when strength, durability and adaptability are priorities.In simple words, cast steel is strong, more durable and versatile, making it a favorite material in industries such as construction, mining, oil and gas and motor vehicles. While advance costs may be high, its ability to handle stress and expand service life often provides better value in a long time.
Different Types of Cast Iron and Cast Steel
Each type of cast iron and cast steel has its own set of properties that make it ideal for certain applications.
Types of Cast Iron:
- Gray Iron: Easy for machines and good at absorbing vibrations. thermal conductivity.
- Ductile Iron: Strong and low brittle, usually used in motor vehicles and pipelines.
- White Iron: Very hard and resistant to wear, best for areas with heavy abrasion.
Types of Cast Steel:
- Carbon Steel: Strong and durable is used for general purposes.
- Alloy Steel: Mixed with elements such as chromium or nickel to improve heat, wear, and corrosion resistance.
Understanding these types highlights the difference cast iron and steel bring to manufacturing and engineering projects, helping industries choose the right material for efficiency and long-term performance.
Choose AKP Ferrocast for Precision Metal Casting and Assembly
Without the Hassle
When it comes to metal components, accurate and reliability is important. The accurate casting ensures that each part meets the accurate specifications, reinventing the function, delay and unnecessary costs. Smooth assembly services simplify further operations, allowing businesses to focus on productivity rather than fit or quality issues.
This is the place where AKP Ferrocast makes a difference. By combining accurate metal castings with streamlined assembly solutions, they help industries achieve constant results with less trouble. Whether it is a complex industrial part or large -scale projects, Choosing partners such as AKP Ferrocast ensures quality, efficiency and peace of mind.
Conclusion
It is not a battle between cast iron vs cast steel as to which is the better material but which is best for a particular job. Cast iron has high compressive strength and heat retention capability. It is widely used in heavy machinery and cookware utensils. On the other hand, cast steel has high tensile strength and is malleable; hence, it is best suited for structural and industrial applications. Depending on whether you require the rigidity of cast iron or the flexibility of cast steel, it is better to understand some of the key differences between cast iron and steel that can guide you in making the right decision. We have a worldwide industrial metals supply of ductile and gray iron to lay a solid base of ductility for your project.
Frequently Ask Questions
What is the primary difference between cast iron and cast steel?
The main difference lies in their carbon content: Cast iron contains carbon between 2% to 4%, while cast steel contains carbon between 0. 15% to 2%. The capacity of cast iron to resist ductility is low compared to cast steel. Cast iron is more brittle, and cast steel is more malleable.
Which material is more corrosion-resistant, cast iron or cast steel?
Cast steel, especially stainless steel, has a higher resistance to corrosion than cast iron, which easily rusts if left untreated.
Can cast iron or cast steel be welded?
The processes of welding cast steel are easier than welding cast iron because cast steel contains a lesser percentage of carbon and is more malleable.
Which is easier to cast, cast iron or cast steel?
Compared to steel, cast iron is easier to cast since it has high fluidity when it is in the molten state and is thus able to make intricate shapes.
Which material is heavier, cast iron or cast steel?
In general, cast iron is heavier than cast steel because of its composition and specifically due to the higher percentage of carbon.
Is cast iron stronger than steel?
Yes, cast iron is stronger.
Is steel heavier than iron?
No, steel is lighter than iron.
