Shell Mould Casting:
Its Overview and Process
Comparison of cast iron vs forged iron reveals some major differences, such as how they are made, their strength, applications, and suitability in any industry. Both forged and cast iron are crucial in metal part production, but knowing each unique characteristic must be selected for your project. Casting vs forging depends on a number of factors, including strength, complexity of shape, and cost-effectiveness.
In this blog, we’ll walk through the differences between cast iron vs forged iron, their properties, applications, and when one’s better than the other. So whether you are designing a product that would demand high strength or make complex shapes, understanding the difference between forged and cast can help you make the best choice.
Table of Contents
What is Shell Mould Casting
Shell moulding casting is a casting process that employs a mould made from a thin layer of sand mixed with a binder, usually a resin. The mould is formed around a pattern of the desired part, and after curing, molten metal is poured into the mould to create the final part. This process is highly effective for producing parts with intricate details and smooth finishes, which is often difficult to achieve using other casting methods.
The main advantage is that it produces good precision metal parts with a minimised post-processing necessity. Shell Mould casting is preferred for aerospace and with high dimensional accuracies and the medical field of applications where higher surface finishes can be ensured without any flaws.
How does it work?
The process of shell mould casting involves several steps to ensure that the final product manufactured will be of high quality. Here is a step-by-step guide on how this technique works:
- Pattern Making: The pattern that has been made from the part to be cast is the first thing that appears. It should be clear that this pattern is typically made up of metal, and the style and scale are quite similar to that of the final product.
- Mould Formation: The pattern is coated with a mixture of sand and resin. Then, the pattern is placed in an oven where it heats up and sets a hard resin mould that keeps the molten metal in place.
- Mould Assembly: The mould is divided into two halves once it is formed. The two halves are placed around the shell pattern in casting, and molten metal is poured between the two halves to fill the cavity of the casting.
- Cooling: Molten metal is allowed to cool and solidify. The mould is broken once it cools, revealing the cast metal part.
- Finishing: This is the last stage that comprises the elimination of surplus material, cleaning up the casting and any other finishing operation if necessary.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Shell Mould Casting
Shell mould casting has several benefits. However, it is a method with weaknesses just like any method. Here are some of the primary strengths and weaknesses of this method used in casting.
- High precision and good surface finish: The main advantage of shell moulding is that they have very tight tolerances and smooth surface finish is that the post-casting machining requirements are minimised.
- Complex geometries: The process is capable of producing intricate parts of complex shapes. It is highly suitable for the aerospace and automobile industries.
- Ductility material compatibility: Shell mould casting can employ the use of both ferrous and non-ferrous. This makes it very versatile.
- Cheap for low and medium quantities: Shell mould casting is cheaper with respect to small to medium-sized production runs since it eliminates the use of expensive reusable moulds, which in turn is considered more pricey compared to die casting.
- Expensive: Shell Mold casting is more expensive than sand casting because the mixture that one uses in shell mould comprises a resin and a mixture of sand.
- Restricted to smaller size: Though workable in complex configurations, shell mould casting is actually done for generating those parts weighing less than 20 kg.
- Complexity for large-sized product casting: Using shell mould casting for mass productions makes the productivity and time spent in that production often very costly, and this equally calls for expensive material consumption in the production since every mould takes a long period of time.
Key Materials Used in Shell Mold Casting
Shell mold casting can hold a broad range of metals, both ferrous and non-ferrous. Among the materials commonly utilised are:
- Carbon Steel: Strength and wear resistance, carbon steel is used for components like camshafts or valve bodies.
- Stainless Steel: This material has high corrosion resistance, so it is used for components in food and medical industries.
- Aluminium Alloys: Lightweight with high conductivity, for use in components in the automobile and aerospace industries
- Copper Alloys: Use where high electrical conductivity is essential, such as electrical connectors, heat exchangers, and more.
Shell Mould Casting vs. Other Casting Methods
Shell mould casting, relative to other casting methods, sheds light on why shell mould casting became the method of choice for some shell mould casting applications. This is a comparative view:
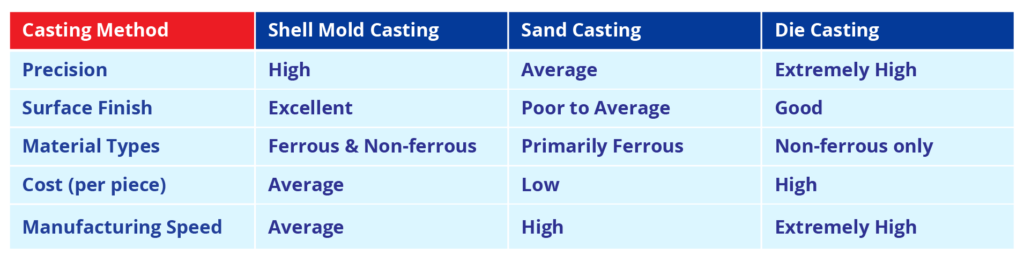
Factors That Influence the Shell Mould Casting Process
The following are elements that influence the result in shell mould casting process:
- Pattern Material: This material generally affects the surface finish, together with the dimensional accuracy of the casting.
- Mould Material: The quality and type of the resin-sand mixture have a direct effect on the final product.
- Metal Pouring Temperature: this is the heat at which a molten metal is poured for uniform filling of Moulds without defects and
- Cooling Rate: Whereby the cooling has an effect upon the properties of hardness and strength, respectively.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, shell mould casting is an excellent option for producing high-precision parts with superior surface finishes. Despite having its own disadvantages, like material costs are high and the speed of production of large parts is slow, the ability to make intricate and accurate castings gives it a place in many industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical. Companies like offer ductile and grey cast iron castings to numerous industries, catering to global demand for high-quality components.
Frequently Ask Questions
Which industries use shell mould casting?
Some of the common industries using shell mould casting for producing high-precision metal components are aerospace, automotive, oil and gas, and medical devices.
How does shell mould casting ensure precision?
Shell mould casting ensures precision through a high-quality resin-sand mixture, which ensures tight tolerances and an excellent surface finish.
What are the main limitations of shell mould casting?
Shell mould casting has several disadvantages, including a high cost for material, a relatively slow speed in producing large pieces, and difficulties in preparing the large mould.
Can shell mould casting be used for large-scale production?
Shell mould casting is cheaper in small and middle runs of production. Yet shell mould casting is applicable in a large production volume. The opposite methods include die casting, which applies to an extremely high number.
