Ferrous Casting vs Non-Ferrous Casting: Differences!
Comparison of cast iron vs forged iron reveals some major differences, such as how they are made, their strength, applications, and suitability in any industry. Both forged and cast iron are crucial in metal part production, but knowing each unique characteristic must be selected for your project. Casting vs forging depends on a number of factors, including strength, complexity of shape, and cost-effectiveness.
In this blog, we’ll walk through the differences between cast iron vs forged iron, their properties, applications, and when one’s better than the other. So whether you are designing a product that would demand high strength or make complex shapes, understanding the difference between forged and cast can help you make the best choice.
Table of Contents
What is Ferrous Metal for Casting?
Ferrous metals are essentially iron, but they can be alloyed with other elements to help enhance their properties. These metals exhibit the greatest tensile strength and durability and are thus used extensively in construction, automobiles, and aerospace.
- Major Characteristics of Ferrous Metals:
- Very high tensile strength and toughness
- Magnetic property
- Prone to rusting and corrosion, unless coated or alloyed.
- Economical and available easily
Some ferrous metals include steel, stainless steel, carbon steel, and cast iron. People have always been puzzled about something whenever material selection comes into play: is cast iron ferrous or non-ferrous? It is one of the ferrous metals that contains iron. Thus it is a ferrous metal.
What is Non-Ferrous Metal for Casting?
Non-ferrous metals do not contain iron. This further signifies that such metals do not rust and corrode easily. They have lesser weight and are ductile in nature, with high electrical and thermal conductivity. These properties prove useful for specialized uses.
Key Properties of Non-Ferrous Metals:
- Lightweight along with resistance to corrosion
- Non-magnetic
- High conductors of heat and electricity
- Extremely malleable, though low tensile strength.
Some of the most commonly known non-ferrous metals include aluminium, copper, brass, zinc, and nickel. Such metals are vastly used in companies involved in the manufacture of aerospace, electrical, and jewellery items.
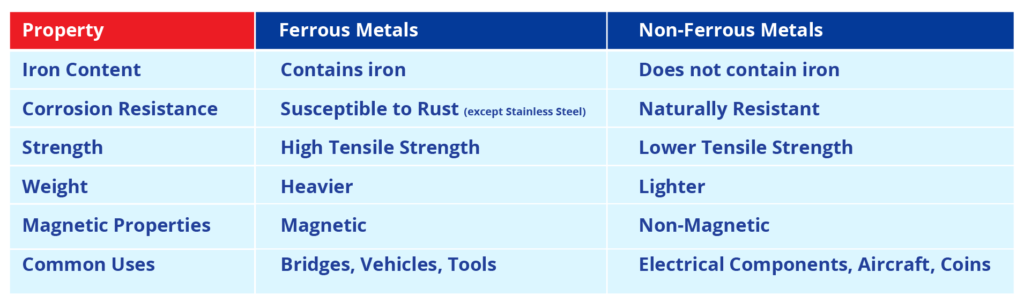
Key Differences Between Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Metals
To choose a suitable casting process, it might be highly required to know some basic differences between ferrous vs non-ferrous materials. Some of the most notable differences have been described above in the following table:
Advantages of Ferrous Metals
Ferrous metals offer many advantages that make it a prime product for several industries:
- Strength and Durability: Used for the most critical stresses, such as in bridges and skyscrapers
- Versatility: Easily alloyed to obtain other desirable properties.
- Cost-effectiveness: Commonly available in massive quantities.
- Magnetic Properties: Crucial in electrical appliances and motors.
These make ferrous metals a beacon in industries that require hard and strong materials.
Advantages of Non-Ferrous Metals
Non-ferrous metals have their own share of benefits, too:
- Resistance to Corrosion: Fine for external and marine applications.
- Light in weight: Applicable to aerospace and automobile parts.
- High conductivity: Applicable for electrical as well as thermal applications.
- Aesthetical value: Often applied for aesthetic and luxury goods.
Their ability and special properties make non-ferrous metals indispensable in modern manufacturing. Applications of Ferrous Casting and Non-Ferrous Metals in Casting. The selection of ferrous metals vs non ferrous metals depends entirely on the application.
Applications of Ferrous Casting
- Beams and columns
- Engines and brakes in automobiles
- Tools and machinery
- Railway tracks and ships
- Applications of Non-Ferrous Casting:
- Electrical wiring and fittings
- Aircraft and space applications
- Jewellery and ornaments
- Plumbing and roofing materials
- Casting Methods for Ferrous Metals
Some of the techniques used for the casting of ferrous metals in order to achieve the desired forms and properties include:
- Sand Casting: It is applied to big, complex pieces.
- Die Casting: It is applied to large volumes of high precision pieces.
- Investment Casting: It is used for intricate designs and thin walls.
- Continuous Casting: It is used for making sheets, rods, and billets.
The above techniques make sure that non-ferrous castings will meet the specifications of various industries.
Casting Techniques Used for Non-Ferrous Metals
Is cast iron ferrous or non ferrous? Special casting techniques are applied on non-ferrous
metals by specifying their unique features in the applications below.
- Gravity Die Casting: They are suited for producing high-density materials
- Centrifugal Casting: Designed for cylindrical products like pipes
- Low-Pressure Casting: Specially suited for aluminium with superior quality
- Vacuum Casting: Specially suited for minimal porosity and exact
Optimizes their exclusive benefits for non-ferrous metals in different applications
The Role of Alloys in Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Casting
Alloys are important not only in perfecting castings made from ferrous as well as non-ferrous metals but also in creating specific characteristics. The desired properties can be strength, corrosion-resistant, and conductivity, among many others, depending on the alloying elements. For example, stainless steel is made from iron, chromium, and nickel, and therefore it is excellent for corrosion resistance.
Common Defects in Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Castings
Both types of castings possess specific defects that can be treated as the leading factors affecting their performance and reliability.
Common Defects in Ferrous Castings:
- Porosity with the entrapment of gas in castings
- Thermal stress cracking
- Shrinkage cavities
Common Defects in Non-Ferrous Castings:
- Oxidation, surface defects
- Inadequate filling of moulds
- Warping due to uneven cooling.
Which Casting Type is Right for Your Project?
The choice between ferrous or non-ferrous casting has a number of parameters as basis.
- Strength versus Weight: Use ferrous metals whenever the application necessitates strength but use non-ferrous materials whenever weight sensitive applications are called for.
- Corrosion Resistance: Use non-ferrous whenever the application is exposed to moisture, chemicals, and more. Be able to weigh both materials and the cost per application within the budget.
If you wish to make the right decision on your project, consult an experienced casting foundry.
Bottom Line
There are so many benefits that castings have to offer. Both ferrous vs non-ferrous are available with different types of applications. Each one would cater to different needs for the project in consideration. So, the difference in their properties must, therefore, be well understood as to how the differences in various properties differentiate their use of both regarding specific metal applications. In conclusion, AKP Ferrocast offers high-quality ductile and grey iron castings to various industries around the world. Their expertise ensures reliable and durable cast iron ferrous or nonferrous solutions for your unique requirements.
Frequently Ask Questions
Can non-ferrous castings handle high-stress applications?
Non-ferrous castings are generally not suitable for high-stress applications due to their lower tensile strength. However, specific alloys may enhance their performance.
What is the role of alloys in ferrous and non-ferrous casting?
Alloys enhance the properties of cast metals, including strength, corrosion and conductivity and are thus used in specialized applications.
Are non-ferrous castings more resistant to corrosion?
Yes, non-ferrous castings have a natural resistance to corrosion. This thus puts them directly into favourable use for marine, outdoor, and chemical environments.
What industries benefit most from non-ferrous casting?
The main applications of non-ferrous castings are aerospace, electrical, jewellery, and plumbing industries, where the material must have the property of being light and anticorrosive.
