Radiographic Testing in Casting: Basics and Benefits Explained
In the world of metal castings, maintaining quality of the product is a non-negotiable priority. Radiographic testing (RT) , a non-destructive test using radiography, has therefore become essential. It enables manufacturers to radiographically screen castings, verifying the final product’s structural if without damaging the object. Within the automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery sectors, even tiny internal defects like shrinkage cavities, porosity, or foreign inclusions could trigger catastrophic failures if concealed. Radiographic testing, therefore, is no longer optional; it is the standard benchmark for internal inspection of castings.
The technique employs either X-rays or gamma rays to generate a wide image of the internal structure of a casting. These radiographs clearly reveal invisible discrepancies to the naked eye, helping engineers and quality inspectors to detect incorporation, hole, or crack defects and spatial distribution. Radiography is particularly powerful for iron casting, where visual inspection and magnetic particle examination fail to provide intensive coverage. By incorporating RT, manufacturers tighten the quality control cycles, the products increase the reliability, and eventually scrap or reduce work.
Let us find the science behind RT, which provides value, and how it piles up against other widely used non-destructive tests (NDT) functioning.
Table of Contents
What is Radiographic Testing?
Radiographic testing (RT) is a non destructive testing method used to check the internal quality of the material. It works by passing high-energy radiation (such as X-rays or gamma rays) through casting to expose any hidden defects.
Before diving into its process, highlight some major aspects of radiographic inspection:
- Non-invasive technology: This test does not change or harm the component being done.
- Image-based analysis: Radiographic inspection creates a visual representation (radiograph) of the interior of the casting.
- Applied to many ingredients: RT works on metals like iron, steel, aluminum, and even composites.
This method helps in detecting radiographic test defects such as:
- Voids and porosity
- Cracks and hot tears
- Slag and oxide inclusion
- Shrinkage cavity
Why is Radiographic Testing Important in Iron Casting?
Radiographic testing is important to maintain the safety, reliability, and performance of cast products. Why is it widely adopted in iron casting processes here:
● Internal defects are detected that do not appear externally
● Ensures structural integrity for safety parts
● Customer improves trust and reduces return rates
● Industry meets standards and compliance requirements
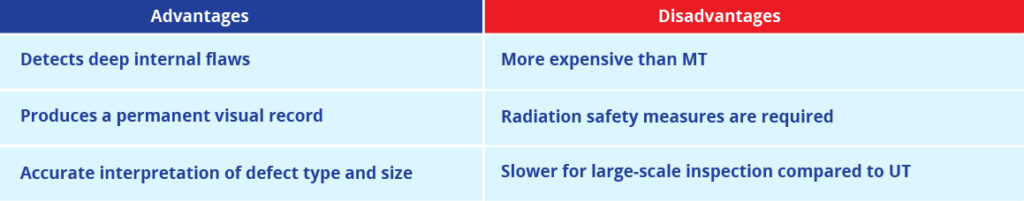
● Provides a permanent record for traceability
● Supports high-volume inspection with digital radiography
By holding the defects quickly, manufacturers avoid expensive rebirth and protect their brand reputation.
How Radiographic Testing Works in Casting
To understand how the radiographic testing method works, let’s break down the process:
- Placement of Component: Casting is positioned between a radiation source (X-ray or gamma ray) and a detector (film or digital sensor).
- Radiation Exposure: The source emits rays that penetrate the material. Internal variations affect how much radiation passes through.
- Image Capture: A radiograph is made by film or digital, which reveals changes in physical density due to defects.
- Interpretation: Certified inspectors evaluate the image to identify defects based on contrast and shape.
Throughout this process, the radiographic testing technique ensures that even hidden flaws deep inside castings can be detected without destruction. Using RT 3-4 times during casting production, especially for critical parts, greatly boosts quality assurance.
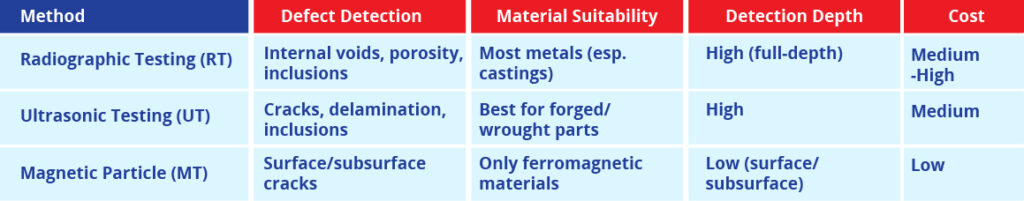
Radiographic Testing vs. Other NDT Methods
It is important to compare RT with other common NDT methods, such as ultrasonic testing (UT) and magnetic particle testing (MT), when it comes to this non-destructive radiography. Each method has its own strengths and limitations.
Advantages And Disadvantages of Radiographic Testing
Digital Radiography in Modern Casting Inspection
With progress in technology, digital radiography is bringing a revolution in radiography inspection. Unlike traditional film-based RT, Digital RT uses flat-panel detectors or imaging plates, and offers:
- Immediate image processing and storage
- Better defect opposite and clarity
- Increased image manipulation and sharing
- Environmentally friendly (no chemical film processing)
Digital RT improves productivity while maintaining the main benefits of radiographic testing.
Common Defects Detected by Radiographic Testing
When inspecting iron casting, a radiographic test helps identify several internal defects:
● Porosity: Small gas pockets that weaken the ingredients
● Shrinkage cavity: voids formed during solidification
● Inclusion: Foreign materials like slag or sand got stuck inside
How they appear on radiographs:
● Porosity appears as light, round spot
● The shrinkage appears as irregular, dark areas
● Inclusion is dense, dark spec or shape
The load-bearing capacity of each part of these radiographic test defects can severely affect and should be addressed before delivery.
Conclusion:
Radiographic testing is one of the most reliable ways to check castings and make sure metal parts are strong and free from hidden defects. This helps manufacturers to detect internal issues that cannot be seen from the outside, which makes production safe, more efficient, and cost effective. This is particularly important in industries where performance and safety cannot be compromised, such as when creating engine blocks or heavy machinery parts.
With the latest digital radiography technology, the process has become even faster and easier. And when combined with other non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, it provides a complete quality control system. At AKP Ferrocast, we use these advanced inspection techniques to help our customers save money, reduce risk, and maintain a strong reputation for quality.
Frequently Ask Questions
What cast materials can be tested with radiography?
Radiography can be used on a wide range of materials including cast iron, aluminum, steel, and bronze.
How deep flaws can be detected in castings?
The radiographic testing can detect deep flaws within the entire thickness of the casting, based on the radiation energy used.
Is radiographic testing safe for casting inspections?
Yes, when proper radiation safety protocol is followed, RT is safe for both operators and environment.
Who can interpret radiographic results in casting?
Only certified radiographic inspectors (eg, ASNT level II or III) should analyze and approve RT results.
Can digital radiography replace film in casting?
Yes, digital radiography provides rapid results, better image quality and short -term costs, making it a rapidly popular option on the film.
