Understanding Cast Iron:
Its Properties, History and Uses
The tale of cast iron dates back to the origins of human civilization. Cast iron boasts a rich history with tales of weaponry and amazing artistry involving iron. While other materials, including steel, aluminum, bronze, brass, and others, have been used for casting purposes, cast iron castings deliver a core advantage on several grounds. Wish to find out, “What is cast iron?” Let us find out!
Table of Contents
What is Cast Iron?
Cast iron is one of the oldest forms of iron used to manufacture several things. Typically, it is a type of iron-carbon alloy featuring a carbon content of more than 2.11 per cent. Cast iron is composed primarily of silicon, iron, and carbon as its core elements. It might also include other materials like sulfur, manganese, and phosphorus in the form of impurities. In some cases, alloying metals are added to improve chemical or mechanical properties of cast iron components.
Types of Cast Iron?
Now that you know about “what is cast iron,” you should also know its types. Cast iron is an iron-carbon alloy that is available in different types based on properties and compositions. Here are some of the common types and insight into how is cast iron made:
1. Ductile Cast Iron
Also known as Nodular Cast Iron, this variant features nodules of graphite to deliver immense flexibility and toughness in comparison to other forms like gray cast iron. Due to these features, ductile cast iron offers excellent tensile strength and impressive impact resistance. These traits also make ductile cast iron perfect for applications involving ample strength or toughness, like for casting automotive parts, crankshafts, gears, and others.

2. Gray Cast Iron
It is one of the most commonly used cast iron variants. As gray cast iron contains graphite flakes in the composition, it is named for its gray color of the fractures. This type of cast iron delivers excellent compressive strength with impressive machinability and limited brittleness. As such, this cast iron finds its applications in the manufacturing of cookware components, pipes, and engine blocks.

3. Malleable Cast Iron
This form of cast iron is produced through heat treatment of white cast iron to change its carbon molecules into irregular nodules rather than flakes. This alteration increases the toughness, ductility, and malleability of the cast iron material. The process improves malleability while minimizing brittleness to create a malleable material that is easily welded, machined, or formed into different shapes.
Due to these traits, malleable cast iron is considered ideal for cast iron uses that require strength and flexibility, like the construction of automotive parts, pipe fittings, or agricultural components.

4. White Cast Iron
This form of cast iron features higher levels of carbon content. The most striking feature of this cast iron is that it is strikingly white throughout and has a shiny appearance. Unlike gray cast iron, which contains graphite for carbon absorption, white cast iron leverages cementite (iron carbide).
The wear-resistant and hard surface of white cast iron makes it perfect for a wide range of wear-intensive applications, like the production of grinding balls and mill liners.

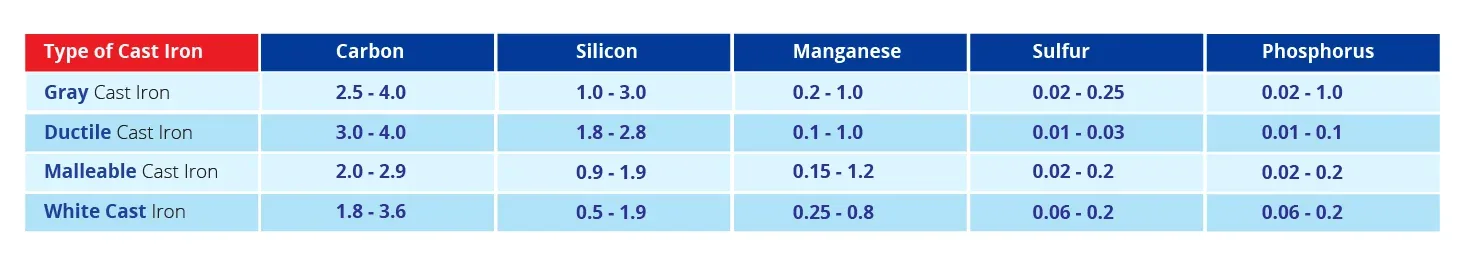
Compositions for Unalloyed Cast Iron Types (in %)
Industrial Uses of Cast Iron
Across the globe, the overall demand for energy-efficient, lightweight, and customized cast iron components is on the rise. With leading cast iron casting manufacturers, like AKP Ferrocast, heading towards expanding the industry, cast iron plays a vital role in the production of various components across diverse industry verticals. Cast iron uses are widespread, including:
Automobile Industry: The most crucial assembly systems and components are manufactured with the help of cast iron. For instance, the engine block is usually manufactured with premium-grade cast iron. Due to its immense durability and mechanical strength, cast iron components deliver reliability to the overall vehicle performance. The dimensional stability of this material is also quite pivotal in this regard. The impressive heat-resistance property of cast iron makes it suitable for use in vehicle motors and engines.
Construction Industry: The sturdiness of cast iron has always been prominent in the construction industry. When sourced from reliable cast iron casting manufacturers and exporters like AKP Ferrocast, the material adds to the overall utility, safety, and durability of construction. In addition to foundational parts like column bases and building bases, cast iron casting components are also utilized in the manufacturing of a wide range of construction-specific applications. These might include gates, manhole covers, water pipes, and much more.
Agricultural Industry: As modern farming procedures continue to evolve, technology has started playing a pivotal role in the given sector. Components made out of premium-grade cast iron are used to deliver efficiency and seamless mobility to agricultural vehicles like tractors. Castings of different shapes and designs are required. Leading cast iron manufacturers and suppliers like AKP Ferrocast ensure seamless delivery of all the required components. In addition to vehicle frames, cast iron casting is also used for the production of other components, including housings, cylinders, drums, and gear castings.
What is the History of Cast Iron
When was cast iron invented or produced? Cast iron owes its origins to China during the 4th century BC. Cast iron was first used in China by the Zhou Dynasty during the periods of spring and autumn. Back then, cast iron was used for the production of war weapons, swords, and iron ploughs.
Cast iron technology first came into Europe during the middle Ages. During the time of the Industrial Revolution in Britain, cast iron was being extensively used for the construction of railway tracks, bridges, and other advanced machinery.
Over time, with the rapid advancement of technology and extensive application, cast iron has since been used in diverse sectors, including agriculture, construction, power generation, and automobiles.
Properties of Cast Iron
The properties of cast iron are shaped by the solidification & cooling processes. The traits of cast iron depend on the speed of cooling, the temperature at which it is poured, the method of injecting molten iron into different moulds, and the moulding procedure. If you are concerned about ‘can cast iron break,” you should learn about its properties.
Here are some properties to look out for:
- High Strength: While cast iron is usually known for its compressive strength due to a higher value for cast iron melting point, the material also boasts its ability to withstand tension. This trait makes it suitable for applications where parts are expected to endure pulling forces.
- Vibration Damping: Vibrations are known to weaken structural units. For most types of cast iron, vibration damping is a crucial feature. Therefore, it finds its applications in the construction of brake calipers.
- Machinability: The high machinability of cast iron, along with its ease of shaping, cutting, and processing through diverse machining methods, is quite renowned. This characteristic finds its application in diverse manufacturing scenarios.
How can AKP Ferrocast Add Value to You?
AKP Ferrocast delivers ample value to the cast iron casting manufacturing industry by leveraging state-of-the-art technology and robust manufacturing facilities. We produce an extensive spectrum of high-quality cast iron products, including agricultural, automotive, and construction equipment for over 45 years.
Our approach integrates cutting-edge technology solutions, including CNC machining and the use of automated sand plants. Moreover, our global reach and ability to meet the diverse needs of our clients through customized cast iron casting services highlight our strategic advantage in the market.
Total Solution In Cast Iron to All Our Clients In Machined Casting Condition
If you are looking for all in one iron casting solutions in machined condition, you can trust our diverse range of cast iron services for diverse industry verticals, including automotive, agriculture, power generation, and construction.
Conclusion
Cast iron is a popular and historic material with a rich history dating back to ancient civilizations. From its high strength to its ability to maintain structural integrity, cast iron finds applications in diverse industry verticals.
Frequently Ask Questions
Cast iron is different from other metals primarily due to its carbon content, ranging typically from 2.2 percent to 4 percent. The presence of high carbon content offers cast iron crucial characteristics like machinability, castability, and fluidity.
Some of the core benefits of cast iron are its resistance to wear, excellent machinability, and impressive vibration damping traits. These properties make cast iron suitable for structural and heavy-duty applications in industries like construction and automotive.
Due to its innate traits like durability, excellent machinability, and wear resistance, cast iron is highly preferred in heavy-duty industries like construction. Cast iron components are able to withstand heavy loads, making it ideal for structural components.
The manufacturing process of cast iron includes melting the iron & its alloy materials. After this, mould preparation, pouring of molten iron into moulds, cooling, and solidification take place.
Both cast irons tend to be different on the grounds of the shape of the graphite particles in the metal. In ductile iron, the graphite is available in the shape of spherical nodules. On the other hand, you will come across graphite flakes in gray cast iron.
