What is CI Casting and
How Does it Work?
CI casting foundry has been a core process of manufacturing for hundreds of years, allowing industries to manufacture complex metal parts with precision, consistency, and effectiveness. The process permits the fabrication of complex geometries that are impossible or difficult to obtain with other methods of fabrication. Among the various casting methods, CI Casting (Cast Iron Casting) is notable for its excellent versatility, strength, and affordability. Cast iron, which contains mainly iron, carbon, and silicon, contains high wear resistance, good thermal conductivity, and higher machinability, making it a most suitable material for numerous applications.
From the automobile and aerospace industries to construction and heavy equipment, CI Casting plays a critical role in shaping industrial parts requiring strength and resilience. Casting intricate designs without undermining structural strength has made cast iron a best-fit material in a wide range of industries.In this blog, we will dig deeper into the fundamentals of CI Casting, its operating principle, forms, advantages, and applications in real life. Apart from this, we shall discuss best practices to assist in manufacturing high-quality cast iron products to meet the changing demands of modern industries. This blog goes through what CI Casting is, how it’s done, different types, advantages, casting information, applications, and best practices to deliver high-quality cast iron products.
Table of Contents
What is Ci Casting?
CI Casting is the process of melting cast iron, which is a mixture of iron, carbon, silicon, and other components, and pouring it into a mould to create a desired shape. After cooling and solidification, the component that is formed has high strength, good thermal conductivity, and wear resistance. This is why cast iron is a choice for producing a vast array of industrial products.
CI Casting is divided into different types based on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the resulting product. The manufacturing process of cast iron is undertaken by melting iron within a furnace, purifying it through addition of required elements, followed by casting molten metal within moulds to achieve required shape and specifications.
What Are The Advantages of CI Casting?
CI Casting has a number of benefits, some of which really lend favour to its usage in several dimensions:
High Strength and Durability- Cast iron has excellent wear resistance, making it a good material for components that undergo high loads and friction. These properties ensure that the working life will be longer while replacements are minimized. Hence, CI casting is ideal in industries such as automotive, construction, and machine-making.
Excellent Machinability- Cast iron is machinable better than most metals, thus lending itself to customization. The microstructure of graphite acts as a lubricant during machining, making the process easier and requiring less abrasive wear on tools that require accuracy and customization.
Cost Effectiveness- The CI casting process has one of the lowest material and production costs, making it definitely an economical and feasible option under mass production.
Good Thermal Conductivity– Cast Iron is also relatively well transmitting and storing heat. That is why CI suits engine components and cooking equipment and in heating systems. Thermal stability offered by certain machining and thermal equipment improves performance.
Corrosion Resistant- Generally, cast iron is inherently a positive repellent to oxidation and degradation due to the environment, hence increasing its life span under adverse conditions. Its natural self-protection against moisture, chemicals, and high temperature, especially in outdoor and industrial applications, means much lesser damage.
Broad Applications- It will cater to a vast gamut because of applications in automobile, aerospace, infrastructure, and home appliances. With the offer of various shapes with varying properties, the usage is adaptable to the diverse engineering needs, and cast iron.
The process of Ci Casting?
Cast iron casting process consists of several steps, from raw material preparation to completion of the final product. The critical steps are:
Raw Material Choice – Production begins by choosing superior grade raw materials, such as pig iron, steel scrap, and alloying elements, based on the desired composition. Raw materials are thoroughly analyzed to ensure compliance with some metallurgical characteristics.
Melting and Refining – The raw materials are refined at high temperatures in a furnace to obtain molten metal. Phosphorus and sulphur impurities are removed during the cast iron casting process to improve the quality of cast iron.
Mould Preparation – A mould is constructed from sand or metal, shaped in line with the requirements of the finished product. Sand moulds are common because they are versatile and inexpensive, while metal moulds are more accurate.
Pouring the Molten Metal – Once the metal is at the ideal temperature and composition, it is poured slowly into the conditioned mould cavity with caution. The operation should be regulated such that turbulence is not induced since it can cause defects such as air pockets and inclusions.
Cooling and Solidification – After being poured, the molten metal gradually cools and solidifies within the mould and adopts its final shape. Cooling rate must be controlled in order to avoid internal stresses and cracking.
Shakeout and Cleaning – After solidification of the casting, the mould is destroyed in retrieving the cast part. Material in excess, i.e., sand or gating system residues, is removed by cleaning processes such as shot blasting or grinding. The process removes impurities from the casting and makes it ready for final finishing.
Machining and Finishing – The last operation is machining the casting to a desired dimension and surface finish. Grinding, polishing, and others are used to impart functionality and appearance. The operation renders the cast iron part ready according to specifications before it is utilized in industry.
Types of of CI Casting?
There are several CI Casting methods, each suitable for particular applications. The well-known ones are:
- Sand Casting– Extremely common process wherein molten iron is poured into sand moulds. Ideally suited to make large and complex shapes.
- Investment Casting – Utilizes wax patterns and ceramic moulds to make precision parts of high accuracy.
- Die Casting – Utilizes high pressure to drive molten iron into metal moulds, which delivers precision along with a smooth surface finish.
- Centrifugal Casting – Utilized to create castings in the form of a cylinder such as pipes and bearings, providing for evenness and strength.
CI Casting vs. Other Metal Casting Methods
Relative to other metal casting methods including steel casting or aluminium casting, CI Casting stands out with the following advantages:
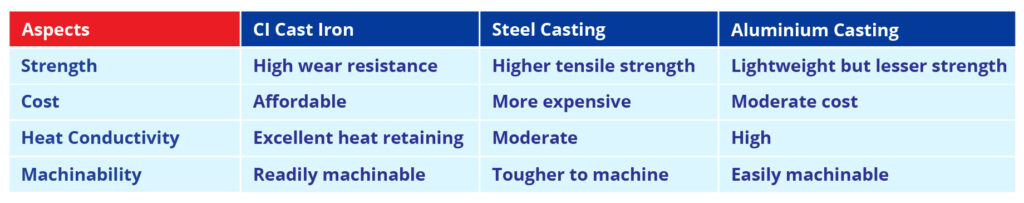
What are Applications of CI Casting?
Application of CI Castings are part and parcel of several industries including:
Automotive Industry – CI Casting plays its important role in automotive casting in producing essential materials such as engine blocks, brake drums, and gearbox parts.
Construction and Infrastructure – Cast iron is the preferred material in the construction casting industry to make pipes, manhole covers, and drainage systems for being corrosion resistant as well as having excellent load-bearing capacity and long life
Aerospace Industry – CI Casting in aerospace applications is meant for use in aircraft components which demand high strength and extreme temperature resistance.
Agricultural and Machinery Use – Heavy-duty CI Cast Agricultural Equipment products , which also nourishes paddy such as ploughs, tractors, and irrigation systems, is built very strong and can withstand harsh handling by farmers.
Energy Sector – The energy industry relies completely on the use of CI Casting in producing components for wind turbines and power plants because of its good thermal properties.
Best Practices for Best Quality CI Casting
- CI Casting manufacturers follow the following best practices to ensure best quality products produced by CI Casting foundries:
- Proper mould Design – Accuracy to avoid defects.
- Optimized Cooling Rates – Control cooling so that no internal stresses are induced.
- Quality Raw Materials- High-grade alloyed iron must be used.
- Inspection Procedures- Non-destructive testing to check for defects.
- Efficient Finishing Operations– South high physical machines for surface smoothening.
Conclusion
CI Casting is the backbone of the metal casting sector, giving rising strengths, affordability, and versatility in one neat package. From car components to industrial machinery, demand for superior cast iron products keeps growing. AKP Ferrocast is an industry leader that exports ductile and gray iron castings to global markets with excellence. AKP Ferrocast ensures businesses will receive-modern dependable cast iron, reliable, effective cast iron products suitable for modern manufacturing needs. AKP Ferrocast offers improved cast iron solutions to meet your industry requirements.
Frequently Ask Questions
Can CI Cast parts be machined or welded?
Yes, casting iron components are easy for machining with regards to its nature. Weldings are said to require preheating and controlled cooling to avoid cracking since it is brittle and suffers from thermal stresses.
How long does CI Casting last compared to steel?
CI Casting parts are long-lasting and resistant and can even last decades when properly maintained. Although steel is stronger in tensile strength, cast iron is extremely durable and has better wear resistance with a longer life span in applications where high stress is not the number one priority.
Which sectors make use of CI Casting most? favoured
Automotive, construction, aerospace, and agricultural sectors are some of those favoured by CI Casting due to its strength, cost-effectiveness, and ability to withstand heavy loads and harsh conditions, hence qualifying it as a multi-purpose material.
