What is Sand Casting and How Does it Work?
Sand casting is also one of the oldest and most widely used methods in manufacturing industries for producing metal components. In this sand casting process, molten metal is poured into a moulded container made of sand to create a desired shape. The mould made from the sand is prepared with the help of a pattern- a replica of the final object. Once the metal cools and solidifies, the mould is broken away to reveal the final product.
This sand moulding process helps create a variety of metal parts, from small, intricate components to large and very complex parts, making it a necessity in the automotive, aerospace, and constructions industries. In this blog, we’ll delve deeper into what sand casting is, the working procedure for sand mould casting, its benefits, and its different applications.
Table of Contents
What is Sand Casting?
Sand casting process is a procedure for casting metals, and sand acts as the mould material. The process works when a mould is created by packing sand around a pattern of the desired shape, into which molten metal is then poured. The mould is then broken away once the metal has cooled and solidified.
The main reason why sand mould casting is so vastly used is mainly because of its flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to work with different metals – aluminium, brass, bronze, and even high-melting-point alloys like steel. This process can be applied for both small-volume production and large-volume manufacturing.
This is no ordinary sand; it’s specialised for molten metals, and thus it should be designed to withstand high temperatures. Generally, sand is mixed with clay, water, and other additives to endow it with the appropriate properties to maintain the form of the mould during casting.
How Does The Sand Casting Process Work?
The sand casting process begins by creating a pattern, which is the exact model of the object to be cast. The pattern is usually made from a material that can withstand the heat of molten metal, such as wax, wood, or metal. This pattern is then put in a box called a “flask” and is covered with sand.
The next step is compacting the sand around the pattern to form a solid mould. The mould is then heated, poured with molten metal, and allowed to cool and solidify inside, forming the desired shape. When cooled, the sand is broken away, leaving the final metal casting.
Key Steps in Sand Casting?
- Pattern creation: A model of the part is created from a material such as wax, metal, or wood
- Preparing the mould: The pattern is placed in a mould box and then covered with a mixture of sand, clay, and water
- Metal Pouring: Molten metal is poured into the mould cavity; it is cooled and allowed to solidify.
- Shakeout: Once cooled, the mould is broken apart to retrieve the casting.
Pros and Cons of Sand Casting Compared To Other Methods
Sand mould casting is considered one of the oldest techniques for casting processes, but it is still widely used due to its simplicity and versatility. Nevertheless, in comparison with other casting methods, there is a need to understand the pros and cons.
Pros of Sand Casting:
- Cost-Effective: Sand casting is considered one of the most cost-effective casting methods for producing a large complex part.
- Versatility: It can be used for a wide range of materials and can produce castings of various sizes and complexities.
- Large Parts: Unlike other casting methods, sand casting is ideal for creating large castings, sometimes weighing several tons.
Cons of Sand Casting:
- Surface Finish: The surface finish of a sand-cast product may not be as smooth as parts produced by other methods, like investment casting.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Sand moulds might only be taken slightly inaccurately since the casting material is unforgiving; post-processing can further fine-tune the finish.
- Labour-Intensive: The method can be slow and may require more manual labour than more automated casting methods.
Benefits of Using Sand Casting In Manufacturing
The advantages of sand casting in manufacturing make it the most preferred method in different industries. If it is a small-size component or a highly complex large-sized piece, sand casting works extremely well and delivers excellent results with flexibility.
- Cost-Effective for Low and High-Volume Production: It is an inexpensive method for low-volume manufacturing as well as high-volume production.
- Wide Material Compatibility:It is widely compatible with materials; for example, ferrous and non-ferrous alloys can be used in the sand-casting process.
- Design versatility: The process can realize complex designs with complicated internal features, such as hollow sections.
- Rapid Prototyping: Because of its relatively low cost to materials, it is best suited for prototyping and testing designs before moving to a more expensive production process.
- Large and Heavy Parts: The process of sand casting is quite helpful in producing large parts that are otherwise cumbersome or impossible to create with other casting techniques.
Sand Casting Explained: Step by Step
Here’s the primary step-by-step process involved in sand casting :
- Pattern Making: A pattern (model) of the part is developed. The pattern is most typically a material designed to be at high temperature, such as metal or wax.
- Mould Preparation: The pattern is mounted in a flask, and sand is packed around the pattern. The sand mixture is compacted to develop a mould, having a gating system to allow molten metal to penetrate the mould.
- Core Formation: A cast is said to need internal features; insert cores in the mould. Cores are usually created from sand and are positioned to outline cavities or passages.
- Pouring Molten Metal: Pour the molten metal into the mould cavity that has been heated to fill the mould, taking on a pattern shape.
- Cooling: The molten metal cools and solidifies inside the mould.
- Shakeout: After the metal has cooled down, the moulding is broken and removed.
- Finishing: Additional processes like grinding, machining, or polishing might be done on the casting to remove excess material and ensure the final product meets all the specifications.
Materials Required For Sand Casting
The following materials are needed to create the moulding and for smooth casting:
- Sand: Special sand with high thermal stability and strength is used.
- Clay: To bind the sand particles together.
- Water: To hydrate the clay and create the required mixture.
- Metal: The molten metal that will fill the mould cavity.
- Binders: Additional materials to improve mould strength, such as organic compounds or chemicals.
Modern Techniques in Sand Casting
Modern sand casting methods have made some great improvements in the efficiency and precision of the sand moulding process. The development of chemical bonding agents enhances the strength and reusability of moulds, which is one such innovation. Another innovation is that 3D printing technology is used to produce patterns and cores whose designs are available and lead to rapid prototyping.
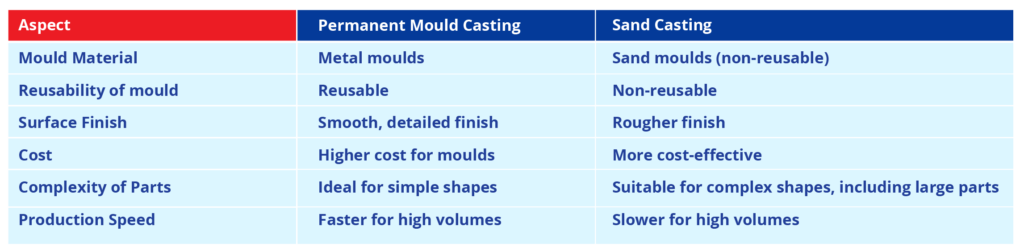
Difference between Permanent Mold Casting vs Sand Casting
Although both are popular casting methods, there are key differences between permanent mould casting and sand casting. Here’s a comparison between types of sand casting:
Bottom Line
Among all casting methods, sand casting is probably one of the most typical. It manages to produce complex, high-quality parts at little cost. From its simplicity and ability to handle a variety of metals, the sand moulding process is essential in many industries. AKP Ferrocast has expertise in producing ductile and gray iron casting, as we serve various industries worldwide by providing top-class quality sand casting services for critical applications.
Frequently Ask Questions
What is sand casting used for?
Sand casting helps fabricate metal parts for the automotive, aerospace, and construction industries, as it is cost-efficient for manufacturing big and complicated metal parts.
What materials are suitable for sand casting?
Aluminum, Bronze, Brass, and Steel are some common alloys used in sand mould casting. More importantly, high-temperature alloys can be cast.
How accurate is sand casting?
Although sand casting is versatile, it might need more precision than better-classed casting processes, such as investment casting, provide. However, this is still sufficiently accurate for most applications.
What industries commonly use sand casting?
Typically, the more significant and intricate metal components are produced via sand casting. The automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery industries need these parts, which is what drives demand for sand casting.
